The intricate process of crafting a diamond involves time, expertise, and resources. Learn and explore the fascinating economics behind these exquisite gems in this guide, so you can make informed purchasing decisions.
How Much Does It Cost to Make a Diamond?
Over the years, the cost of growing a carat of diamond has experienced a dramatic shift. Back in 2008, the process incurred a substantial expense of approximately $4000. Yet, in the present day, the introduction of the CVD method has brought about a remarkable transformation.
Now, cultivating one carat of diamond demands merely $200 to $500, making it a much more affordable and viable option. This advancement has opened up new possibilities for diamond enthusiasts to enjoy the beauty of these precious gems without breaking the bank.
What is the Process of Growing a Diamond in a Lab?
Growing diamonds in a lab, a process known as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), has revolutionized the diamond industry by offering an alternative to naturally mined diamonds.
This innovative technique allows scientists to create high-quality diamonds in controlled environments, mimicking the natural conditions that give rise to these precious gems. Let’s explore the fascinating process of growing diamonds in a lab.

Seed Selection
The first step in the CVD process is selecting a suitable diamond seed. A diamond seed acts as a foundation upon which the new diamond will grow. These seeds are typically small, high-quality diamond fragments that provide the necessary lattice structure for the carbon atoms to align during the growth process.
Preparation of the Growth Chamber
Creating diamonds in a lab requires a specialized growth chamber. The chamber is typically made of a high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) environment, designed to replicate the conditions found deep within the Earth where natural diamonds form.
The chamber is then filled with a hydrocarbon gas, often methane, and heated to extreme temperatures.
Activation of Gas and Diamond Growth
Once the growth chamber is prepared, the hydrocarbon gas inside is activated by introducing energy, such as microwaves or hot filaments. The energy breaks down the gas molecules, releasing carbon atoms.
These carbon atoms are then transported to the diamond seed, where they begin to accumulate, layer by layer, forming a diamond crystal over time.

Controlling Growth Parameters
Achieving high-quality diamonds requires precise control over various growth parameters. Factors such as gas pressure, temperature, and the ratio of carbon to hydrogen atoms are meticulously adjusted to influence the growth rate and crystal quality.
This level of control ensures the formation of large, flawless diamonds with desirable characteristics.
Cooling and Removal
After the diamond reaches the desired size, the growth chamber is slowly cooled down to stabilize the crystal lattice structure. Once the process is complete, the newly grown diamond is carefully removed from the chamber.
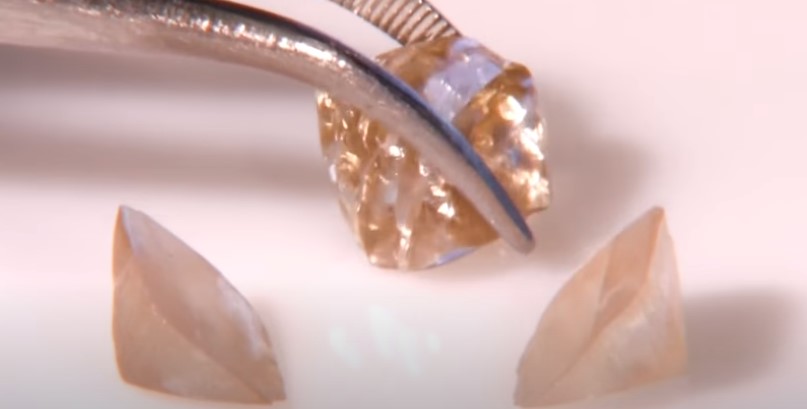
Cutting and Polishing
The rough diamond obtained from the CVD process is still in its raw form and needs cutting and polishing to unlock its brilliance fully. Skilled artisans use traditional diamond cutting techniques to shape the rough stone into a faceted gem, ready to be set into jewelry or used in various industrial applications.
What Influences the Cost of Making a Diamond?
The cost to make a diamond is influenced by a multitude of factors, spanning from the type of diamond being produced to the intricacy of the manufacturing process.
Understanding these key determinants sheds light on the economics behind diamond production. Below are the significant factors that greatly influence the cost of making a diamond.
Type of Diamond
The type of diamond being produced has a profound impact on the cost. Natural diamonds, formed deep within the Earth over millions of years, require extensive mining operations, which can be both financially and environmentally demanding.
In contrast, lab-grown diamonds, created through advanced technological processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) techniques, often have lower production costs, making them a more budget-friendly alternative.
Manufacturing Method
The manufacturing method employed to create diamonds significantly affects the cost. Traditional methods, such as mining for natural diamonds, involve substantial expenses related to exploration, excavation, and labor.
Conversely, lab-grown diamonds, while requiring initial investment in technology and equipment, tend to have more streamlined and controlled production processes, reducing overall costs.

Quality and Size
The quality and size of the diamond play a crucial role in determining its cost. Higher-quality diamonds with desirable characteristics, such as clarity, color, and cut, command a premium price.
Additionally, larger diamonds, which are relatively rare, are more expensive to produce compared to smaller ones due to the higher raw material requirements and longer growth times.
Market Demand
Market demand and supply dynamics have a direct influence on diamond prices. If there is a surge in consumer demand for diamonds, especially for specific shapes, colors, or sizes, the cost to make these diamonds may increase to meet the market’s needs.
Conversely, a decrease in demand may result in lower prices as producers strive to remain competitive.
Certification and Brand
Certification from reputable gemological laboratories and the influence of a renowned brand can significantly impact the cost of a diamond. Certified diamonds with well-established provenance and branding tend to carry higher price tags due to the assurance of quality and authenticity they offer to consumers.

Why is Diamond So Expensive?
Diamonds are known for their exquisite beauty and timeless allure, but their high price tag is driven by several key factors. Firstly, natural diamonds, formed deep within the Earth over billions of years, are incredibly rare and challenging to extract.
The mining process requires substantial investment in exploration, excavation, and labor, contributing to the overall cost. Additionally, the quality of a diamond greatly influences its price. Diamonds with exceptional clarity, color, and cut are scarce and highly sought after, commanding premium prices in the market.
Furthermore, the diamond industry is heavily influenced by demand and branding. Diamonds have been historically associated with luxury and romance, making them a symbol of status and affection. As a result, consumer demand for diamonds remains high, and renowned brands with a strong reputation in the market can further drive up prices.
While lab-grown diamonds offer a more cost-effective alternative, the allure of natural diamonds’ rarity, timelessness, and emotional significance [1] continues to justify their higher price point in the eyes of many consumers.
Conclusion
The cost of making a diamond varies based on factors such as the type of diamond (natural or lab-grown), manufacturing method, quality, and market demand, influencing accessibility and affordability.

