Replacing an irrigation valve is a crucial task to maintain an efficient watering system. The cost varies depending on factors such as valve type, labor charges, and materials.
We will delve into the key considerations that influence the expenses involved in this process, helping you make informed decisions for your irrigation system’s maintenance.
How Much Does It Cost to Replace an Irrigation Valve?
Irrigation valve replacement expenses can differ significantly due to factors like valve type, damage extent, job complexity, and property location. On average, you can expect costs ranging from $100 to $400 per valve.
Evaluating these aspects beforehand will help you plan and budget effectively for your irrigation system’s maintenance.
What is an Irrigation Valve?
In a water sprinkler system, an irrigation valve is a key element that controls the flow of water to the sprinkler heads. It is typically an electronically controlled or manually operated device that opens and closes to allow or restrict the water flow to specific zones of the sprinkler system.
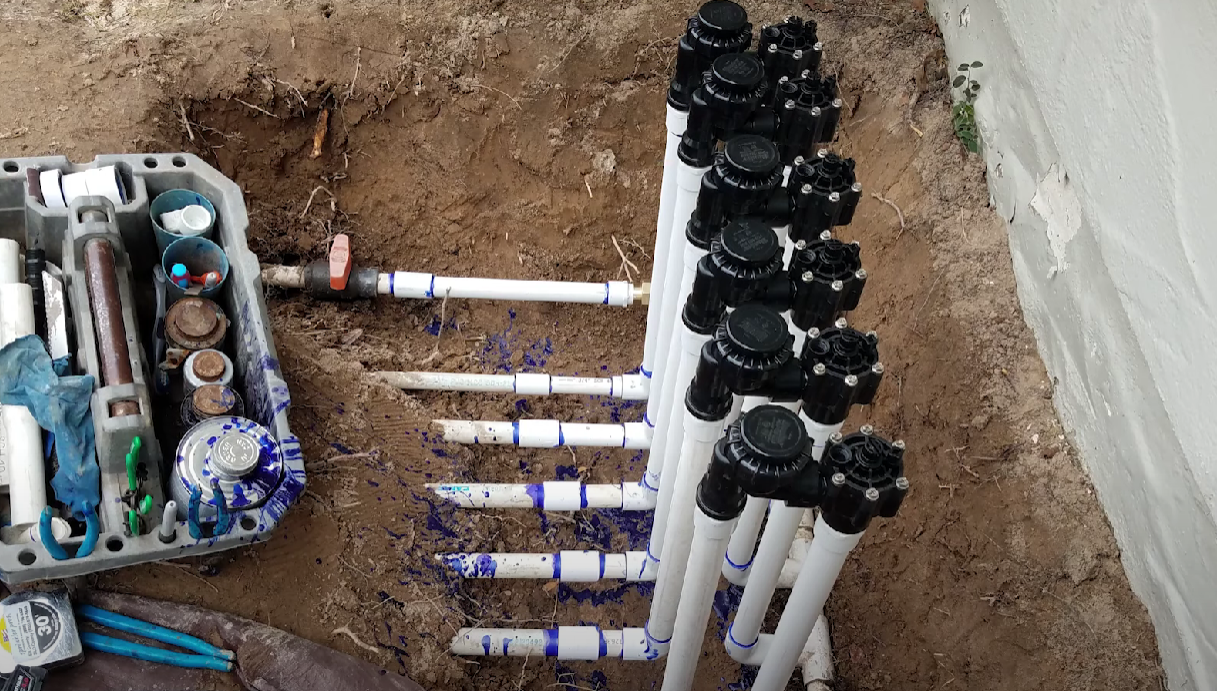

Each zone represents a designated area in the landscape that requires watering. By using irrigation valves, the sprinkler system can efficiently deliver water to different parts of the garden or lawn, allowing for targeted and customizable irrigation schedules.
What Causes an Irrigation Valve to Leak?
Irrigation valves are essential components in maintaining an efficient watering system for landscapes and agricultural fields. However, like any mechanical device, irrigation valves are susceptible to wear and tear, and one common issue that can arise is leakage.
Understanding the causes behind irrigation valve leaks is crucial in preventing water wastage, minimizing damage, and ensuring the proper functioning of the irrigation system.
Below are the various reasons that can lead to irrigation valve leaks, along with possible solutions to address each problem effectively.
Age and Wear
One of the primary reasons irrigation valves may develop leaks is age and wear. Over time, valves are subjected to constant use, exposure to the elements, and water pressure fluctuations, causing the internal components to deteriorate.
O-rings, seals, and gaskets can become worn or brittle, leading to small gaps or cracks that result in leaks. The older the valve, the higher the likelihood of such issues occurring.

Regular maintenance and inspection of older valves are essential to identify and address potential problems before they escalate into significant leaks.
Improper Installation
Improper installation is another common cause of irrigation valve leaks. If the valve is not fitted correctly into the irrigation system, it can lead to misalignment or faulty connections, resulting in water seepage.
In some cases, over-tightening or under-tightening of connections during installation can cause damage to the valve or compromise the sealing, leading to leaks.
Hiring a professional irrigation technician for installation can help avoid these issues and ensure that the valve is correctly integrated into the system.
High Water Pressure
Excessive water pressure within the irrigation system can strain the valve’s internal components, causing them to wear out more quickly and develop leaks. If the system operates at a pressure level above the valve’s design limit, it can put stress on the valve’s seals and gaskets, leading to failure and leakage.
Installing a pressure regulator in the irrigation system can help maintain the water pressure within the recommended range and protect the valves from damage due to high pressure.

Sediment and Debris
Sediment and debris in the water supply can also contribute to irrigation valve leaks. When small particles or debris accumulate within the valve, they can interfere with the sealing mechanism, causing leaks to occur.
Moreover, sand, silt, and other particles can cause abrasion and wear on the valve’s internal components, leading to further leakage issues. Regularly flushing the irrigation system and installing appropriate filtration systems can help prevent sediment and debris from causing damage to the valves.
Freeze Damage
In regions with cold climates, freezing temperatures can pose a significant threat to irrigation valves. When water within the valve freezes, it expands, putting immense pressure on the valve’s internal structure.
This can lead to cracks or fractures in the valve body or other components, resulting in leaks once the ice thaws. Using freeze-resistant or anti-siphon valves, along with proper winterization techniques, can help protect irrigation valves from freeze damage.
Chemical Damage
Certain chemicals present in the water supply, such as those from fertilizers or pesticides, can be corrosive to the materials used in irrigation valves. Continuous exposure to these chemicals can lead to the degradation of valve components, including seals and gaskets, causing leaks over time.
Using valves specifically designed to resist chemical damage or installing a chemical injection system at a safe distance from the valves can help minimize this risk.

Root Intrusion
In some cases, plant roots can intrude into the irrigation system, including the valve assemblies. As roots grow, they can exert pressure on the valve components, leading to cracks or displacements that allow water to escape and cause leakage.
Regularly inspecting the irrigation system and employing root barriers or keeping plants at a safe distance from the valves can prevent root intrusion issues.
Physical Damage
Physical damage, such as accidental impacts from lawnmowers, gardening tools, or other machinery, can cause leaks in irrigation valves. A cracked valve body or damaged internal components can lead to water seepage and reduce the valve’s effectiveness.
Being cautious while working around the irrigation system and placing protective barriers or covers over the valves can help prevent physical damage.
What Are the Signs That an Irrigation Valve Needs to Be Replaced?
A well-functioning irrigation valve is crucial for the efficient watering of landscapes and agricultural fields. However, like any mechanical component, irrigation valves can deteriorate over time and develop issues that affect their performance.
Recognizing the signs that an irrigation valve needs replacement is essential to avoid water wastage, prevent damage to the irrigation system, and ensure optimal water distribution.
Below are the key indicators that suggest an irrigation valve requires replacement, along with the appropriate steps to address these signs and maintain a reliable irrigation system.
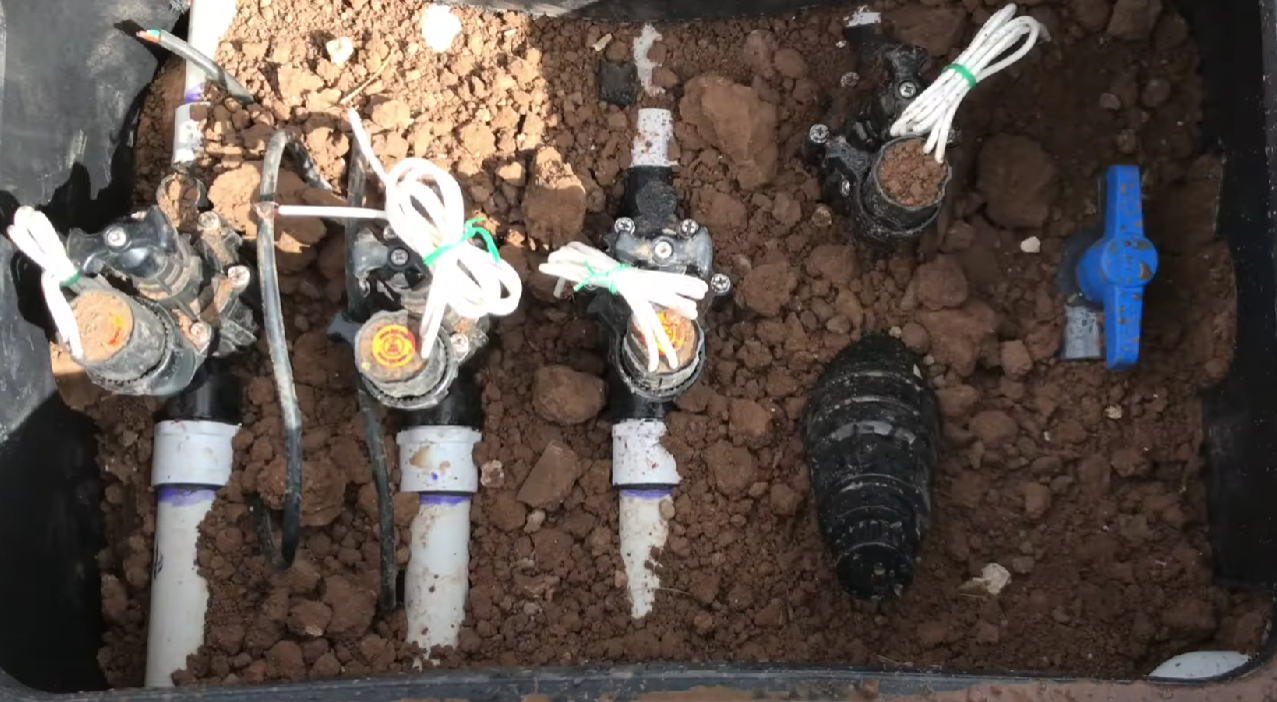

Continuous Water Leakage
One of the most apparent signs that an irrigation valve needs replacement is continuous water leakage. If you notice water pooling around the valve, damp spots in the landscape, or a constant stream of water from the valve even when the system is turned off, it indicates a leak in the valve assembly.
Leaks can result from worn-out seals, cracked valve bodies, or damaged internal components. Ignoring such leaks not only wastes water but can also lead to waterlogging, overwatering, and potential landscape damage.
Inconsistent Water Flow or Pressure
When an irrigation valve is no longer functioning correctly, it may lead to inconsistent water flow or pressure within the system. You might notice certain areas of your landscape receiving inadequate water while others are overwatered.
This imbalance in water distribution is often indicative of a faulty valve that is not fully opening or closing as intended. If you observe variations in water pressure across different zones, it’s essential to inspect the valves and consider replacement if necessary.
Valve Fails to Open or Close
Another clear sign that an irrigation valve needs replacement is when it fails to open or close as expected. If a valve remains stuck in the closed position, it will prevent water from reaching the designated zone, leading to under-irrigation and potential plant stress.
Conversely, if the valve remains stuck in the open position, it will cause continuous water flow, resulting in water wastage and increased utility bills. A malfunctioning valve that no longer responds to the irrigation system’s commands should be replaced promptly.
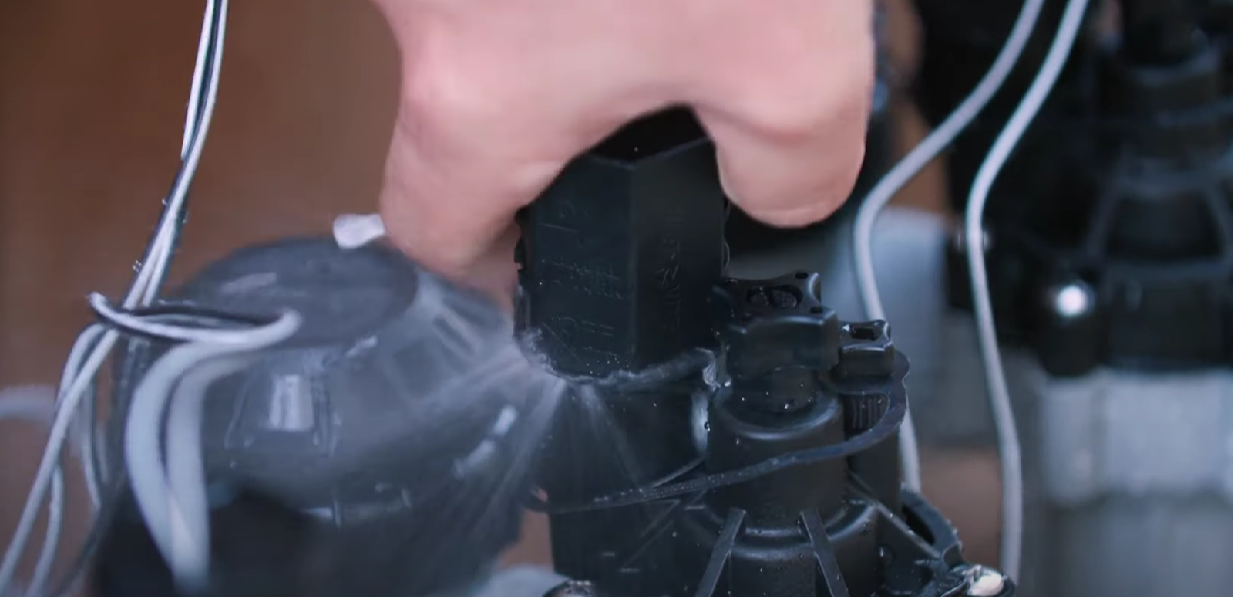

Audible Clicking or Vibrations
During normal operation, irrigation valves may emit a faint clicking sound when opening or closing. However, if you notice loud clicking noises or vibrations emanating from the valve, it could indicate mechanical issues.
Excessive clicking or vibrations may suggest worn-out components or debris interfering with the valve’s proper functioning. If left unattended, these problems can worsen and lead to valve failure, necessitating replacement.
Valves Staying Open After System Shutdown
After turning off the irrigation system, the valves should close promptly to stop the flow of water. If you observe that one or more valves continue to remain open after the system has been shut down, it is a sign of valve malfunction.
This can lead to water leakage and overwatering, potentially causing water-related problems in your landscape. Replacing the faulty valve will prevent further water wastage and ensure efficient irrigation management.
Reduced Coverage or Dry Patches
A declining performance in irrigation coverage, resulting in dry patches or areas in the landscape, may indicate valve issues. When valves are no longer functioning optimally, they may fail to deliver the expected amount of water to specific zones, leading to inadequate irrigation and visible dry spots.
If adjusting the irrigation schedule or cleaning the nozzles does not resolve the problem, it might be an indication that the valve requires replacement.
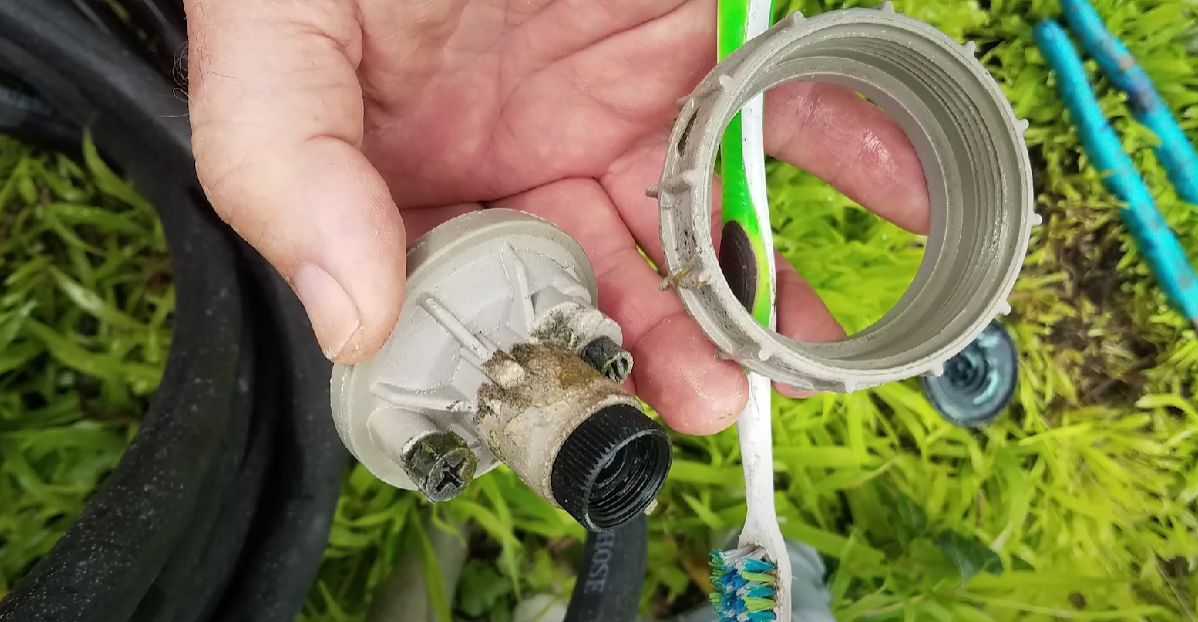

Age and Wear
Age is an essential factor in assessing the condition of an irrigation valve. As valves age, their internal components, such as seals, gaskets, and diaphragms, can deteriorate, leading to leaks and operational problems.
Even with regular maintenance, the wear and tear of older valves can become increasingly challenging to manage effectively.
If your irrigation system incorporates valves that are several years old, it might be a prudent decision to consider replacing them with newer and more reliable models.
Repair Complexity and Frequency
Frequent repairs or a series of complex issues with an irrigation valve may indicate that it has reached the end of its lifespan. While minor repairs are common in irrigation systems, recurring or significant problems might suggest that the valve has become unreliable and requires replacement.
Repeatedly repairing an aging valve may prove more costly and time-consuming in the long run than investing in a new, durable valve that offers improved performance.
What Are the Cost-Related Factors in Replacing an Irrigation Valve?
Replacing an irrigation valve is a necessary maintenance task to ensure the efficient functioning of an irrigation system. However, the cost of valve replacement can vary significantly based on various factors.
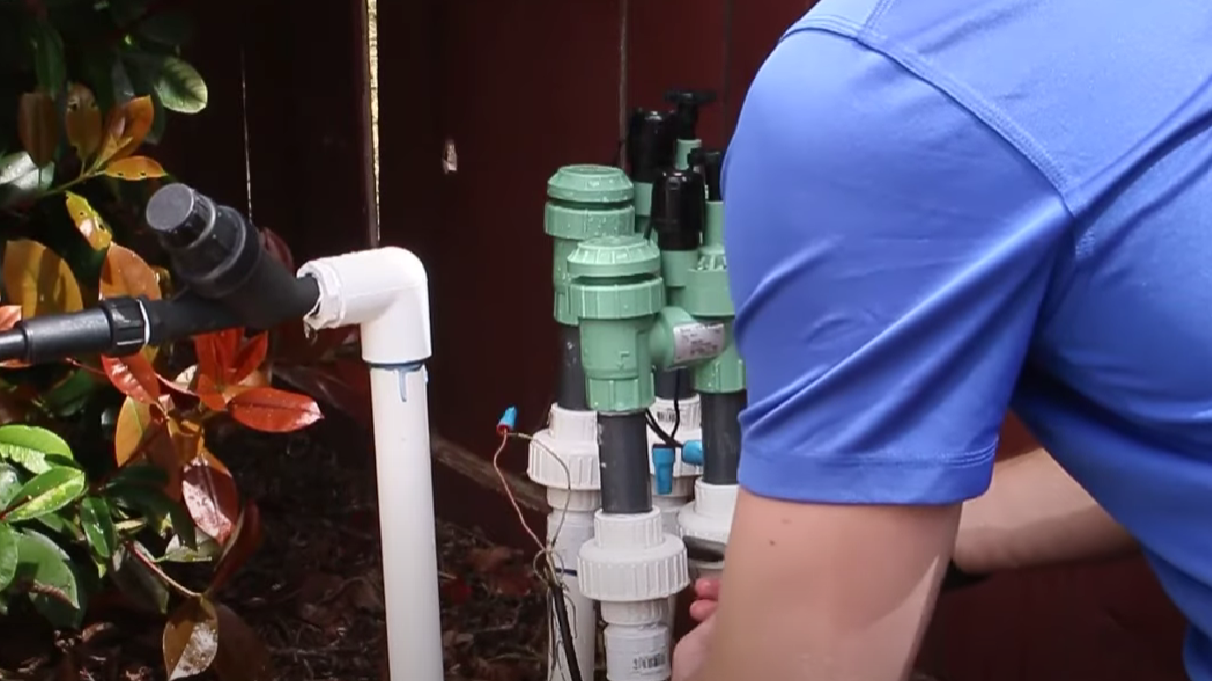

Understanding these cost-related factors is essential for budgeting and making informed decisions about your irrigation system’s maintenance. Below are the key factors that influence the cost of replacing an irrigation valve.
Type of Valve
The type of irrigation valve you choose significantly impacts the overall replacement cost. There are various types of valves available, including globe valves, angle valves, anti-siphon valves, and electric solenoid valves, among others.
Each type serves specific purposes and comes with varying price points. Simple manual valves are generally more affordable compared to electronically controlled solenoid valves, which provide automation and remote control capabilities.
Before deciding on a replacement valve, consider the specific needs of your irrigation system and the features required, as this will influence the cost.
Quality and Brand
The quality and brand of the replacement valve can also affect the cost. Valves from reputable brands that offer better durability and reliability may come at a higher price point.
While it can be tempting to opt for cheaper alternatives, investing in a higher-quality valve can save money in the long run, as they are less likely to develop issues and may require less frequent replacement.

Labor Charges
The cost of labor for replacing an irrigation valve is another significant factor to consider. Hiring a professional irrigation technician ensures the job is done correctly, minimizing the risk of future problems and potential water wastage.
Labor charges can vary depending on the complexity of the job, the location of the valve, and local labor rates. It’s advisable to obtain quotes from multiple technicians to compare costs and select a qualified professional who offers a fair price for the services.
Extent of Damage
In some cases, the need for an irrigation valve replacement arises due to damage beyond repair. The extent of damage to the existing valve can impact the cost of replacement.
If only a specific component of the valve is faulty, such as a seal or diaphragm, the cost may be lower as compared to replacing the entire valve assembly. Regular maintenance and prompt repairs can help identify and address minor issues before they escalate into more extensive and costly problems.
Number of Valves
The total number of valves that need replacement directly affects the overall cost. If you have multiple valves that require replacement, the expense can quickly add up.
On the other hand, replacing a single valve is a more cost-effective solution. It’s essential to assess the condition of all the valves in your irrigation system during maintenance checks to identify any potential replacements needed.

Accessibility of Valves
The accessibility of the valves within the irrigation system can impact the cost of replacement. Valves located in hard-to-reach or confined spaces may require additional effort and time for removal and installation.
Technicians may need specialized equipment or have to make adjustments to reach the valves, which can increase labor charges. Consider the location of the valves when estimating the replacement cost.
Additional Materials
In addition to the replacement valve itself, there may be other materials needed for the installation process. These can include piping, fittings, adapters, and anti-siphon devices.
Depending on the specific requirements of your irrigation system, these additional materials can contribute to the overall replacement cost. A thorough assessment of the system and consultation with the technician will help determine the necessary materials for the replacement job.
Contractor Experience
The level of experience and expertise of the irrigation contractor can also impact the replacement cost. Established and experienced professionals may charge higher rates due to their track record of quality work and customer satisfaction.
While choosing a contractor solely based on cost may seem appealing, it’s essential to consider their reputation, qualifications, and customer reviews to ensure a successful and efficient replacement process.

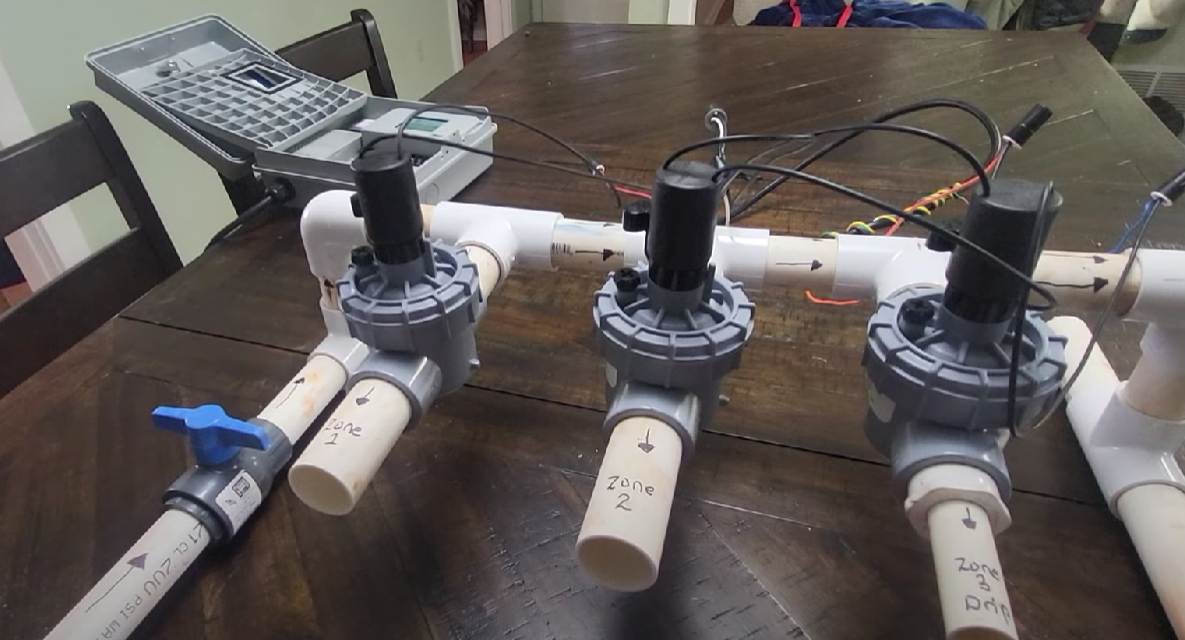
What Are the Different Types of Irrigation Valves?
Irrigation valves are essential components of any efficient watering system, controlling the flow of water to different zones in a landscape or agricultural field. There are several types of irrigation valves available, each designed to serve specific purposes and cater to varying irrigation needs.
Understanding the different types of irrigation valves can help you choose the most suitable option for your irrigation system. Below are the various types of irrigation valves, their features, and their applications, providing valuable insights to enhance your irrigation system’s performance.
Globe Valves
Globe valves are one of the most commonly used types of irrigation valves. They feature a globe-shaped disc that moves up and down to regulate the water flow through the valve.
When the valve handle is turned, the disc lifts off the seat, allowing water to pass through. These valves offer precise control over the flow rate and can be adjusted to provide different water pressure levels to various zones in the irrigation system.
Globe valves are suitable for both residential and commercial applications, making them a versatile choice for many irrigation setups.
Angle Valves
Angle valves, also known as 90-degree angle valves, are similar to globe valves but have an angled design. The inlet and outlet of the valve are positioned at a 90-degree angle to each other.
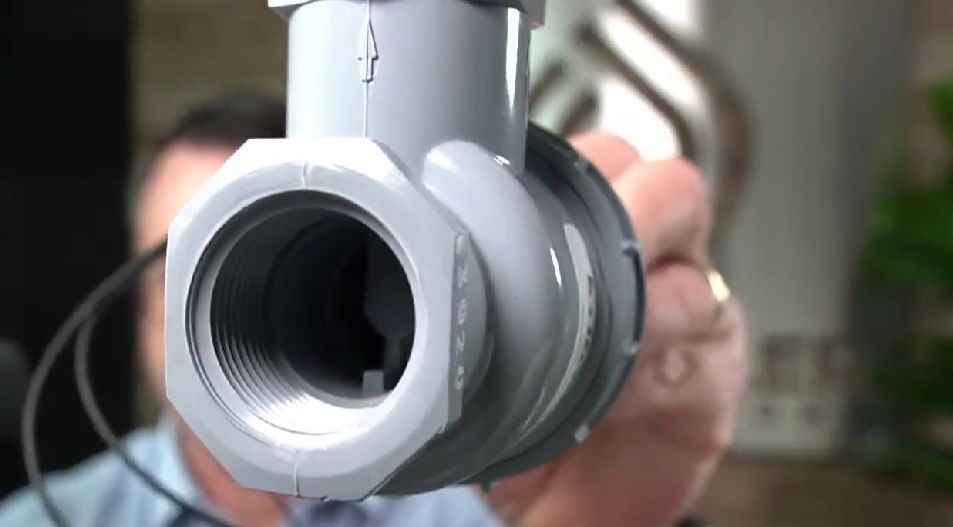

This configuration allows for easier installation in tight spaces or corners where straight-line valves may not fit. Angle valves are commonly used in irrigation systems that require water flow to change direction efficiently.
Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm valves are a type of on/off valve that uses a flexible diaphragm to control water flow. When the valve is open, the diaphragm is lifted, allowing water to pass through.
Closing the valve pushes the diaphragm back down, stopping the flow. These valves are commonly used in automatic irrigation systems and are ideal for precise control over water flow and shut-off capabilities.
Diaphragm valves are resistant to clogging and are often used in systems that handle water with sediment or debris.
Ball Valves
Ball valves feature a spherical ball with a hole through its center that regulates water flow. When the valve handle is turned, the ball rotates to align the hole either parallel or perpendicular to the water flow, allowing for on/off control.
Ball valves provide a full bore opening, minimizing pressure loss and maximizing flow rate. They are reliable, easy to use, and suitable for both residential and commercial irrigation systems.
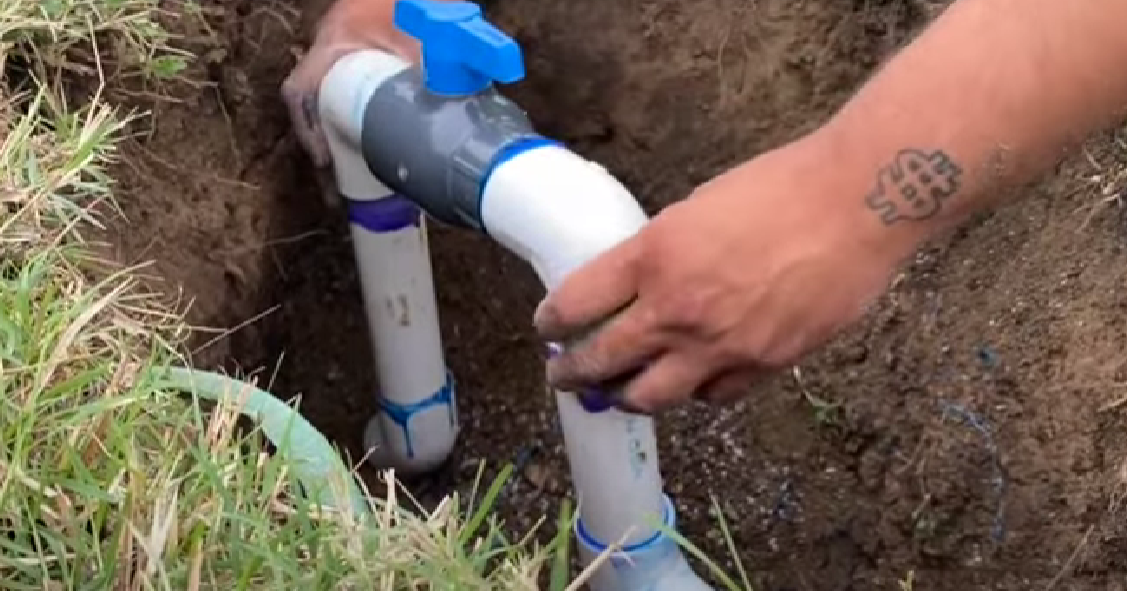

However, ball valves are primarily designed for on/off applications and may not offer the same level of flow control as other valve types.
Gate Valves
Gate valves are another type of on/off valve commonly used in irrigation systems. They feature a gate-like disc that moves up and down to control the flow of water. When the valve is fully open, the gate is lifted completely out of the way, allowing unobstructed water flow.
These valves provide minimal pressure loss and are suitable for applications where a full-bore opening is required. However, gate valves are not recommended for precise flow control, as they are more prone to leaks and do not offer the same level of adjustability as globe or diaphragm valves.
Anti-Siphon Valves
Anti-siphon valves are specialized valves designed to prevent water from flowing back into the main water supply. They are commonly used in above-ground irrigation systems and prevent the risk of contamination by ensuring that water only flows in one direction.
Anti-siphon valves are often used in residential sprinkler systems, and they include a built-in backflow preventer, eliminating the need for a separate backflow prevention device.
These valves are typically installed at a higher elevation than the highest sprinkler head to create a siphon break.
Electric Solenoid Valves
Electric solenoid valves are electronically controlled valves that allow for remote operation and automation of the irrigation system. They feature an electromechanical solenoid that, when energized, lifts a plunger to open the valve.
When the power is cut off, the plunger returns to its resting position, closing the valve. Electric solenoid valves can be integrated into smart irrigation systems, allowing users to schedule watering times, adjust flow rates, and monitor the system remotely.
While they offer convenience and precision control, electric solenoid valves are typically more expensive than manual valves.
Pressure-Regulating Valves
Pressure-regulating valves, as the name suggests, are designed to maintain a constant water pressure downstream of the valve. They help prevent over-pressurization in the irrigation system, protecting sensitive components such as drip emitters and micro-sprinklers from damage.
These valves are especially useful in systems with varying water pressure levels or where pressure fluctuations are common.
How to Prolong the Life of an Irrigation Valve?
Irrigation valves play a vital role in the proper functioning of an irrigation system, regulating water flow and distribution to different zones. To ensure an efficient and long-lasting irrigation system, it is essential to take measures to prolong the life of irrigation valves.
Regular maintenance, proper installation, and implementation of preventive practices can significantly extend the lifespan of these critical components. Below are effective ways to prolong the life of an irrigation valve, helping you optimize the performance and longevity of your irrigation system.
Conduct Regular Inspections
Regular inspections are fundamental to identifying any issues with the irrigation valves promptly. Conduct thorough checks of all valves in the system, looking for signs of leaks, wear, or damage.
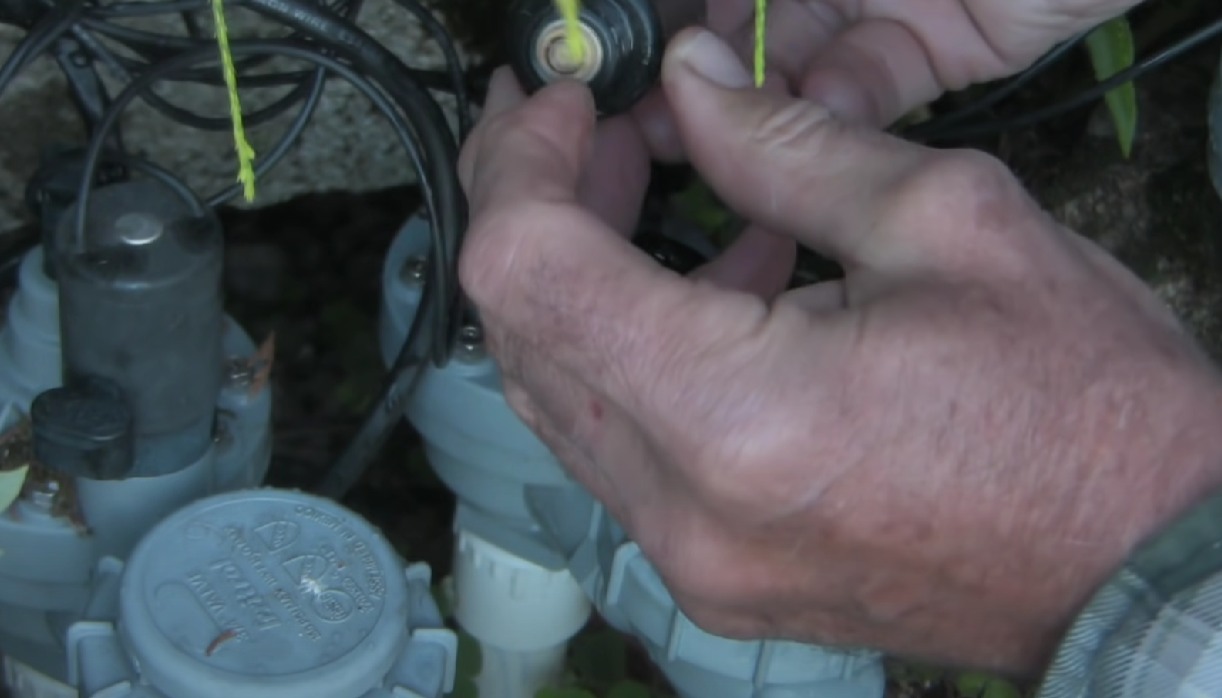

Pay attention to visible signs of water leakage around the valves, unusual noises, or reduced water flow. Addressing potential problems early on can prevent further damage and extend the life of the valves.
Clean and Flush the System
Regularly cleaning and flushing the irrigation system can help remove debris, sediment, and mineral deposits that can clog the valves and affect their performance.
Install proper filtration systems to trap large particles and regularly clean or replace filters as needed. Flushing the system periodically will prevent build-up and ensure smooth water flow, minimizing the risk of damage to the valves.
Use Pressure Regulators
Excessive water pressure can strain irrigation valves, leading to premature wear and leaks. To protect the valves from high pressure, use pressure regulators in the system.
Pressure regulators ensure that the water pressure remains within the recommended range, reducing stress on the valves and other system components.
Optimize Water Quality
Water quality can significantly impact the lifespan of irrigation valves. Water containing high levels of minerals, salts, or other contaminants can cause corrosion and deterioration of valve components.
If your water supply has poor quality, consider using a water treatment system or filtration devices to improve water quality before it reaches the irrigation system.

Choose High-Quality Valves
Investing in high-quality valves from reputable brands can pay off in the long run. High-quality valves are more durable and less prone to wear, providing better performance and a longer lifespan.
While they may have a higher upfront cost, the reduced need for repairs and replacements will result in long-term savings.
Install Backflow Preventers
Backflow preventers are essential devices that protect the irrigation system from potential contamination. They prevent water from flowing back into the main water supply, safeguarding the system from pollutants and chemicals.
By using backflow preventers, you can prevent damage to the valves and other components caused by contaminated water.
Implement Winterization
Proper winterization is crucial for protecting irrigation valves in regions with freezing temperatures. Before winter sets in, drain the irrigation system to remove any water from the valves and pipes.
Freezing water can expand and cause damage to the valves, leading to leaks or cracks. Taking the necessary steps to winterize the system will prevent freeze-related issues and extend the life of the valves.
Avoid Physical Damage
Be mindful of potential physical damage to the irrigation valves. Ensure that the valves are placed in locations where they are less susceptible to accidental impacts from lawnmowers, gardening tools, or other equipment.
Placing protective barriers or covers over the valves can provide an additional layer of protection.
Choose Suitable Valve Types
Selecting the right type of valve for each zone in your irrigation system can also contribute to their longevity. Consider factors such as flow control requirements, water pressure, and the specific irrigation needs of each zone.

Utilizing appropriate valve types ensures that the system operates optimally and reduces stress on the valves.
Hire Professional Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial to the longevity of irrigation valves. Hiring a professional irrigation technician for installation ensures that the valves are correctly integrated into the system and minimizes the risk of errors that could lead to early failure.
Regular maintenance by professionals helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, keeping the valves in good working condition for an extended period.
How Often Do Irrigation Valves Need to Be Replaced?
The frequency of replacing irrigation valves depends on several factors, including the type of valve, the quality of the valve, the maintenance practices, and the overall usage of the irrigation system.
Generally, well-maintained and high-quality irrigation valves can last anywhere from 10 to 15 years or more. Manual valves, such as globe valves and gate valves, tend to have a longer lifespan as they have fewer mechanical components prone to wear.
On the other hand, electronically controlled valves, like electric solenoid valves, may have a shorter lifespan due to the additional electronic components that can be more susceptible to failure.
How Do You Fix an Irrigation Valve?
Fixing an irrigation valve requires a systematic approach to identify and address the specific issue affecting the valve’s performance. Here is a general guide to fixing common problems with irrigation valves:
Identify the Issue
Begin by inspecting the valve and the surrounding area for any visible signs of leaks, damage, or irregularities. Check for water puddles, wet spots, or audible sounds that may indicate leaks.

Shut Off the Water
Before working on the valve, turn off the water supply to the irrigation system. This will prevent any water flow during the repair process.
Clean the Valve
Debris, sediment, and mineral deposits can cause clogging and affect the valve’s operation. Clean the valve and its components thoroughly to ensure unobstructed water flow.
Inspect the Valve Components
Examine the diaphragm, seals, gaskets, and other components for signs of wear or damage. Replace any worn-out parts with suitable replacements.
Address Leaks
Leaks are common issues in irrigation valves. Replace damaged seals, O-rings [1], or diaphragms to fix leaks and ensure a watertight seal.
Adjust the Flow Control
If the valve is not allowing sufficient water flow, check the flow control adjustment. Adjust the flow control screw or mechanism to achieve the desired water flow.
Clear Obstructions
Sometimes, debris or small stones may obstruct the valve’s operation. Clear any obstructions that prevent the valve from opening or closing properly.

Check for Electrical Issues
If you are dealing with an electric solenoid valve, check the wiring and the solenoid for any electrical issues. Ensure that the wiring is properly connected and that the solenoid is functioning correctly.
Replace the Valve
In some cases, if the valve is severely damaged or has reached the end of its lifespan, replacing the entire valve may be the most effective solution.
Test the Valve
After completing the repair, turn on the water supply and test the valve to ensure it is functioning correctly. Check for leaks, proper opening, and closing, and adjust the flow control as needed.
Conclusion
The cost of replacing an irrigation valve can vary depending on factors such as the valve type, extent of damage, labor charges, and materials. On average, the expenses can range from $100 to $400 per valve.
Evaluating these considerations beforehand will aid in making informed decisions for maintaining an efficient irrigation system.

