Embarking on a journey beyond Earth’s bounds has always captivated our imagination. But have you ever wondered about the price tag that comes with building a spaceship?
From groundbreaking technologies to mind-boggling engineering feats, join us as we uncover the astronomical costs that fuel our aspirations to conquer the final frontier.
How Much Does It Cost to Build a Spaceship?
With an impressive investment of $10.6 billion, NASA spearheaded the awe-inspiring development of the Space Shuttle. This colossal sum encompassed not only the creation of the shuttle itself but also its essential counterparts like the solid rocket boosters, external tanks, and the remarkable RS-25 main engines.
Furthermore, an additional $444 million was allocated toward constructing state-of-the-art facilities for the production, launch, and processing of these groundbreaking spacecraft.
In today’s dollars, when adjusting for inflation, the monumental venture is estimated to reach a staggering $49 billion, marking an extraordinary testament to human ingenuity and ambition.
Factors That Influence the Cost of building a spaceship
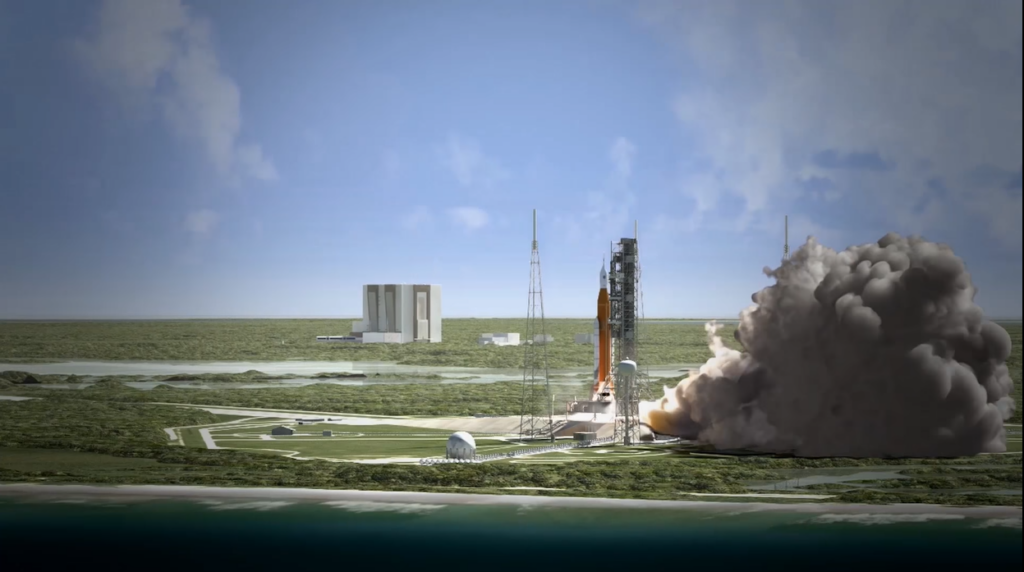

Several factors come into play when determining the cost to build a spaceship. The complexity and scale of such a project necessitate a careful analysis of various elements that contribute to the final price tag. Here are some key factors that can influence the cost of building a spaceship.
Mission Objectives
The nature and scope of the spacecraft’s mission significantly impact the cost. Different missions require different capabilities, such as orbiting Earth, lunar landings, deep space exploration, or even manned missions.
Each objective comes with its own set of technical requirements, which directly affect the complexity and cost of the spacecraft.
Design and Engineering
The spacecraft’s design is crucial in terms of functionality, safety, and efficiency. A well-thought-out and meticulously engineered design can help optimize resources and minimize costs.
However, complex mission requirements, such as the need for advanced propulsion systems, robust life-support systems, or radiation shielding, can increase both design and engineering expenses.
Materials and Technology
The choice of materials and technology incorporated into the spacecraft affects its performance, durability, and overall cost. Cutting-edge materials, such as lightweight composites or heat-resistant alloys, often come with a higher price tag.
Similarly, incorporating state-of-the-art technology, like advanced avionics, communication systems, or propulsion mechanisms, can significantly increase costs but may be necessary for achieving mission objectives.
Manufacturing and Testing
The actual construction of a spacecraft involves a myriad of manufacturing processes and quality control measures. The complexity of the spacecraft design, the need for specialized components, and the level of precision required in manufacturing all contribute to the overall cost.
Additionally, rigorous testing and verification procedures to ensure reliability and safety can add significant expenses.
Launch Vehicle
A crucial factor in space missions is the selection of an appropriate launch vehicle. The cost of the launch vehicle, which includes production, fueling, and launch operations, is a substantial component of the overall cost.
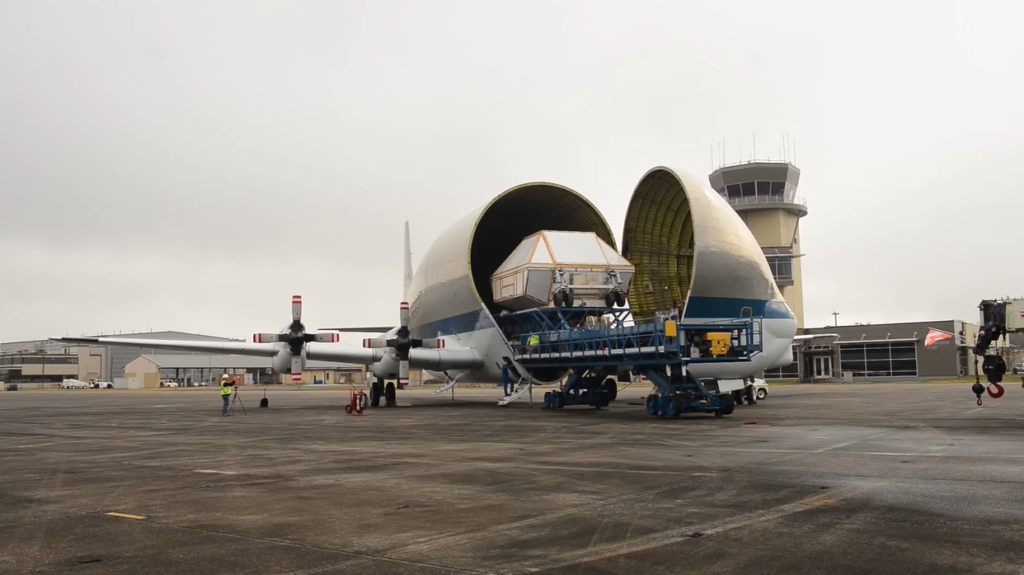

The choice of launch vehicle depends on payload capacity, required trajectory, and the destination of the spacecraft.
Research and Development
Before the actual spacecraft construction begins, extensive research and development activities are undertaken. This involves theoretical studies, computer simulations, prototype testing, and iterative design improvements.
The cost of research and development can be substantial, especially for innovative and groundbreaking missions that push the boundaries of current space exploration capabilities.
Scale and Quantity
The scale and quantity of spacecraft being produced can influence costs. Building a single prototype or a small batch of spacecraft can be more expensive per unit than producing them in larger quantities.
Economies of scale, where costs decrease as production volumes increase, can be achieved through mass production techniques, standardized components, and streamlined manufacturing processes.
Infrastructure and Facilities
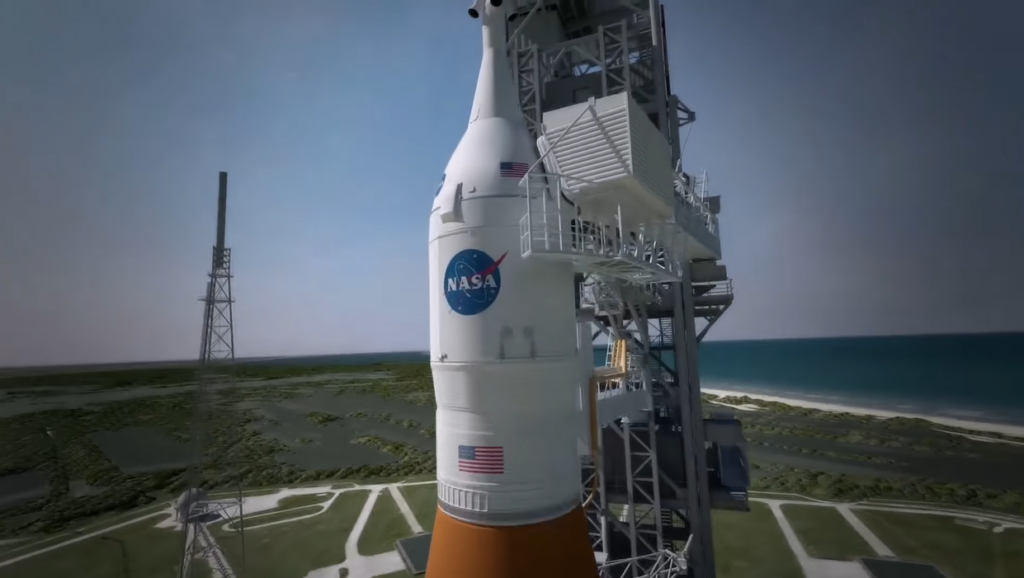

Establishing and maintaining the necessary infrastructure and facilities to support spacecraft construction and operations require significant investments. This includes research and development centers, production facilities, launch pads, mission control centers, and testing facilities.
The cost of building and maintaining these infrastructures is a crucial factor in the overall cost of a spacecraft program.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Spacecraft development must adhere to stringent regulations and safety standards. Meeting these requirements involves additional costs for safety assessments, compliance audits, and ensuring adherence to international space treaties [1].
Safety measures, redundancy systems, and fail-safe mechanisms are implemented to minimize risks, but they can contribute to increased costs.
Timeframe and Schedule
The timeline for developing and building a spacecraft also affects the cost. Shorter deadlines may require increased resources, more workforce, and expedited procurement, leading to higher costs.
Balancing schedule constraints with budget considerations is crucial to ensure a realistic and efficient spacecraft development process.
Conclusion
The cost of building a spaceship is influenced by various factors such as mission objectives, design complexity, materials, technology, infrastructure, and regulatory compliance, making it a significant investment in the human exploration of space.

